Introduction
In the fast-paced world of financial technology (fintech), efficient customer onboarding and robust regulatory compliance are critical for sustainable growth. Traditional Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are often slow, manual, and prone to errors, leading to customer frustration and operational inefficiencies. Enter electronic KYC (e-KYC), a digital solution that leverages modern technologies to streamline identity verification while ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements. This article explores how e-KYC is reshaping fintech onboarding and compliance, the technologies that underpin it, the challenges involved, and best practices for successful implementation.
Definition
E-KYC (Electronic Know Your Customer) is a digital process used by businesses and financial institutions to verify the identity of their customers remotely. It leverages electronic documents, biometric data, and online verification methods to streamline customer onboarding, enhance security, and reduce paperwork compared to traditional KYC procedures.
Understanding e-KYC
Electronic Know Your Customer, or e-KYC, is the process of using digital channels to confirm a customer’s identification. Unlike the outdated “wet signature” methods or paper-based document checks, e-KYC employs automated workflows, biometric authentication, and secure digital document exchange. Customers can complete the entire verification process online – often within minutes – by submitting photos of identification documents and real-time facial scans. This digital-first approach reduces the reliance on physical documentation, accelerates verification timelines, and creates a smoother experience for both customers and financial institutions.
The Importance of KYC in Fintech
The prevention of fraud, money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illegal financial activity depends on KYC standards. Regulatory bodies across the globe mandate financial institutions and fintech companies to verify and validate the identity of their customers before providing services. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in heavy fines, legal consequences, and reputational damage.
Enhancing Customer Onboarding
Frictionless User Experience:
E-KYC platforms integrate seamlessly with mobile apps and web portals. Customers simply snap a photo of their ID and take a selfie, and the system guides them through any additional steps. Adaptive user interfaces can detect poor image quality or non-compliance with guidelines, prompting users to retake photos. This interactive feedback loop minimizes errors and drop-offs, resulting in higher completion rates.
Real-Time Verification:
Traditional KYC processes may involve manual reviews that can take hours or days. e-KYC systems leverage machine learning algorithms and databases of sanctioned entities to perform instant checks. For example, optical character recognition (OCR) extracts data from ID documents, while face match algorithms confirm that the person presenting the ID is its legitimate owner. Compliance personnel are informed of problems in real time, allowing for prompt remediation.
Seamless Integration:
Modern e-KYC providers offer APIs and Software Development Kits (SDKs) that integrate with existing core banking systems, CRM platforms, and onboarding workflows. This integration means fintech firms can deploy e-KYC quickly without overhauling their entire technology stack, reducing implementation costs and time to market.
Scalability:
As fintech companies grow, they may onboard thousands of customers per day. e-KYC solutions are built on cloud infrastructures that scale elastically, handling peak loads without degradation in performance. Automated workflows ensure that no additional human resources are needed as volume increases, keeping operational costs predictable.
Strengthening Compliance
Automated AML and PEP Screening:
e-KYC solutions incorporate automated screening against global watchlists, politically exposed persons (PEP) databases, and adverse media sources. These checks are updated in real time, ensuring that fintech firms remain compliant with evolving regulatory landscapes. Any positive match triggers an alert, which is escalated to compliance officers for further investigation.
Audit Trails and Record-Keeping:
One of the significant advantages of e-KYC is the creation of immutable digital records. Every step of the verification process—document submission, biometric match, screening results—is time-stamped and logged. These audit trails are essential during regulatory inspections or when responding to investigations, as they provide clear evidence of due diligence.
Adaptive Risk Scoring:
Advanced e-KYC platforms employ risk-based approaches to customer verification. Low-risk customers (e.g., domestic retail users with no adverse history) may undergo simplified checks, while high-risk profiles (e.g., foreign entities, politically exposed persons) trigger enhanced due diligence, such as additional document verification or manual review. This targeted approach balances customer experience with regulatory rigor.
Data Privacy and Security:
Compliance isn’t limited to AML/CTF regulations—data protection laws like GDPR in Europe and similar frameworks worldwide mandate strict controls on personal data. End-to-end encryption, safe data storage, and strict access controls are all used by e-KYC providers to protect client information. Consent management features ensure that users understand how their data is used and stored, fostering trust.
Core Technologies Behind e-KYC
Optical Character Recognition (OCR):
OCR extracts textual information from scanned IDs, passports, and utility bills. High-accuracy OCR engines reduce manual data entry errors and accelerate data capture.
Biometric Authentication:
Facial recognition and liveness detection confirm that the person presenting the document is physically present and matches the ID photo. Advanced algorithms detect spoofing attempts, such as photographs or masks, ensuring authenticity.
Machine Learning and AI:
Beyond OCR and biometrics, AI-driven modules analyze document integrity (e.g., detecting counterfeit holograms) and perform named-entity recognition for more effective AML screening. Machine learning models learn from previous verification results to continuously increase accuracy.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledgers:
Some fintech innovators are exploring blockchain for secure, decentralized identity management. Blockchain’s immutable ledger can store hashed identity attributes, allowing customers to share verified credentials without exposing sensitive data.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Digital Divide:
Not all customers have access to high-quality smartphones or reliable internet connections. To mitigate this, fintech firms can offer hybrid processes—allowing customers to upload images via low-bandwidth channels or visit partner branches for assisted digital onboarding.
Regulatory Fragmentation:
e-KYC solutions need to adjust to different jurisdictions’ rules. Working with providers that offer configurable compliance rulesets and region-specific screening data helps fintech companies remain agile in global markets.
Data Privacy Concerns:
Customers may hesitate to share personal information online. A clear consent process, minimal data collecting guidelines, and open communication about data security measures can all help allay privacy concerns.
False Positives and Negatives:
While slack systems might overlook real threats, overly stringent screening can mark legitimate users as high-risk. Regular tuning of machine learning models, combined with periodic human reviews, strikes the right balance between accuracy and user experience.
Best Practices for Implementing e-KYC
Choose the Right Vendor:
Evaluate providers based on accuracy, speed, global coverage, data security certifications, and integration flexibility. Proof-of-concept trials help assess real-world performance.
Adopt a Phased Rollout:
Begin with a pilot for a specific customer segment or region. Gather metrics on onboarding speed, verification success rates, and customer feedback before scaling to the entire user base.
Train Internal Teams:
Ensure compliance officers, customer support, and IT personnel understand the e-KYC workflow. Cross-functional training accelerates issue resolution and fosters ownership.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization:
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as average verification time, drop-off rates, false-positive rates, and regulatory audit outcomes. Utilise these realisations to enhance procedures and configurations.
Customer Education:
Provide clear instructions, FAQs, and tutorial videos to guide users through the digital onboarding process. Proactive support reduces confusion and enhances satisfaction.
The Future of E-KYC in Fintech
The future of e-KYC looks promising with continuous innovations:
-
Decentralized Identity: Users could control their own identity data via blockchain-based digital identities, allowing selective sharing of verified credentials.
-
Enhanced AI: More sophisticated AI models will improve fraud detection and automate more complex verification tasks.
-
Global Standardization: Efforts are underway to harmonize KYC regulations across borders, simplifying compliance for fintech companies operating internationally.
-
Integration with Other Technologies: Combining e-KYC with biometrics, digital signatures, and real-time risk scoring will create fully automated and highly secure onboarding ecosystems.
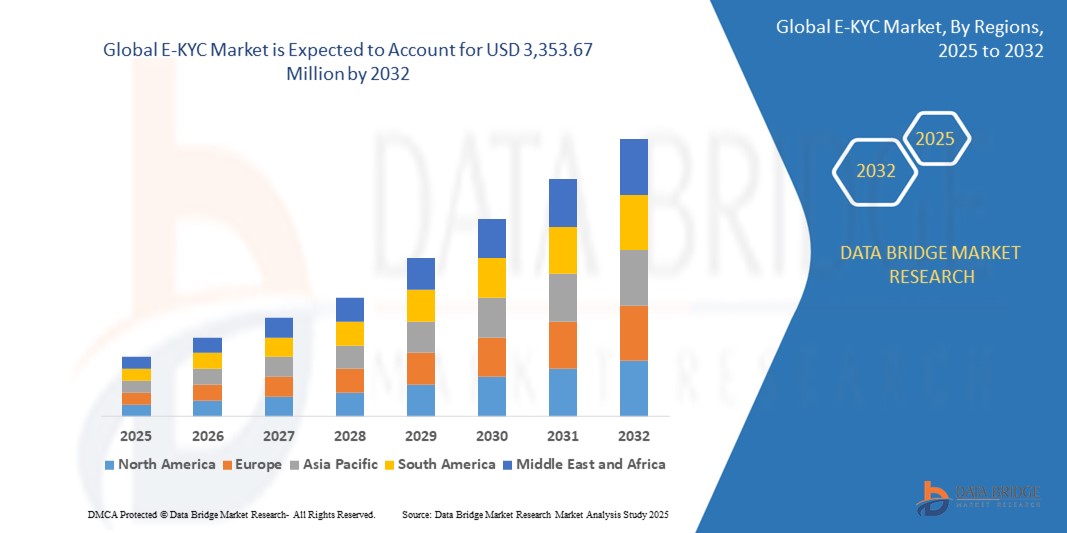
Growth Rate of E-KYC Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.62%, the worldwide e-KYC market is projected to grow from its 2024 valuation of USD 800 million to USD 3,353.67 million by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-e-kyc-market
Conclusion
E-KYC is no longer a futuristic concept but a current necessity in the fintech landscape. It enables financial companies to onboard customers swiftly and securely while meeting rigorous regulatory standards. The adoption of e-KYC drives operational efficiency, improves customer experience, and mitigates risks associated with fraud and non-compliance.